Steroid 11β-hydroxylase
| CYP11B1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | CYP11B1, CPN1, CYP11B, FHI, P450C11, cytochrome P450 family 11 subfamily B member 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | OMIM: 610613; MGI: 88584; HomoloGene: 128035; GeneCards: CYP11B1; OMA:CYP11B1 - orthologs | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| EC number | 1.14.15.4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| steroid 11β-monooxygenase | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| EC no. | 1.14.15.4 | ||||||||
| CAS no. | 9029-66-7 | ||||||||
| Databases | |||||||||
| IntEnz | IntEnz view | ||||||||
| BRENDA | BRENDA entry | ||||||||
| ExPASy | NiceZyme view | ||||||||
| KEGG | KEGG entry | ||||||||
| MetaCyc | metabolic pathway | ||||||||
| PRIAM | profile | ||||||||
| PDB structures | RCSB PDB PDBe PDBsum | ||||||||
| Gene Ontology | AmiGO / QuickGO | ||||||||
| |||||||||
Steroid 11β-hydroxylase, also known as steroid 11β-monooxygenase, is a steroid hydroxylase found in the zona glomerulosa and zona fasciculata of the adrenal cortex. Named officially the cytochrome P450 11B1, mitochondrial, it is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CYP11B1 gene.[5][6] The enzyme is involved in the biosynthesis of adrenal corticosteroids[7] by catalyzing the addition of hydroxyl groups during oxidation reactions.
Gene
The CYP11B1 gene encodes 11β-hydroxylase, a member of the cytochrome P450 superfamily of enzymes. The cytochrome P450 proteins are monooxygenases that catalyze many reactions involved in drug metabolism and synthesis of cholesterol, steroids and other lipids. The product of this CYP11B1 gene is the 11β-hydroxylase protein. This protein localizes to the mitochondrial inner membrane and is involved in the conversion of various steroids in the adrenal cortex. Transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been noted for this gene.[6]
The CYP11B1 gene is reversibly inhibited by etomidate[8][9] and metyrapone.
Function
11β-hydroxylase is a steroidogenic enzyme, i.e. the enzyme involved in the metabolism of steroids. The enzyme is primarily localized in the zona glomerulosa and zona fasciculata of the adrenal cortex. The enzyme functions by introducing a hydroxyl group at carbon position 11β on the steroid nucleus, thereby facilitating the conversion of certain steroids.
Humans have two isozymes with 11β-hydroxylase activity: CYP11B1 and CYP11B2.
CYP11B1 (11β-hydroxylase) is expressed at high levels and is regulated by ACTH, while CYP11B2 (aldosterone synthase) is usually expressed at low levels and is regulated by angiotensin II. In addition to the 11β-hydroxylase activity, both isozymes have 18-hydroxylase activity.[10] The CYP11B1 isozyme has strong 11β-hydroxylase activity, but the activity of 18-hydroxylase is only one-tenth of CYP11B2.[11] The weak 18-hydroxylase activity of CYP11B1 explains why an adrenal with suppressed CYP11B2 expression continues to synthesize 18-hydroxycorticosterone.[12]
Here are some of the steroids, grouped by catalytic activity of the CYP11B1 isozyme:
Cortisol and corticosterone metabolism
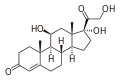
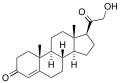
11β-hydroxylase has strong[13] catalytic activity during conversion of 11-deoxycortisol to cortisol and 11-deoxycorticosterone to corticosterone, by catalyzing the hydroxylation of carbon hydrogen bond at 11-beta position. Note the extra "–OH" added at the 11 position (near the center, on ring "C"):
Mechanism of action
As a mitochondrial P450 system, P450c11 is dependent on two electron transfer proteins, adrenodoxin reductase and adrenodoxin that transfer 2 electrons from NADPH to the P450 for each monooxygenase reaction catalyzed by the enzyme. In most respects this process of electron transfer appears similar to that of P450scc system that catalyzes cholesterol side chain cleavage.[25] Similar to P450scc the process of electrons transfer is leaky leading to superoxide production. The rate of electron leakage during metabolism depends on the functional groups of the steroid substrate.[26]
Regulation
The expression of the enzyme in adrenocortical cells is regulated by the trophic hormone corticotropin (ACTH).[27]
Clinical significance
A mutation in genes encoding 11β-hydroxylase is associated with congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 11β-hydroxylase deficiency.
11β-hydroxylase is involved in the metabolism of 17α-hydroxyprogesterone to 21-deoxycortisol,[17] in cases of congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency.[28][29]
See also
Additional images

-
 Corticosteroid biosynthetic pathway in rat
Corticosteroid biosynthetic pathway in rat -
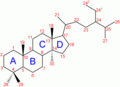 Steroid numbering
Steroid numbering
References
- ^ a b c GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000160882 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ a b c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000022589 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ Lifton RP, Dluhy RG, Powers M, Rich GM, Gutkin M, Fallo F, et al. (September 1992). "Hereditary hypertension caused by chimaeric gene duplications and ectopic expression of aldosterone synthase". Nature Genetics. 2 (1): 66–74. doi:10.1038/ng0992-66. hdl:11577/133580. PMID 1303253. S2CID 975796.
- ^ a b
 This article incorporates public domain material from "Entrez Gene: CYP11B1 cytochrome P450, family 11, subfamily B, polypeptide 1". Reference Sequence collection. National Center for Biotechnology Information. Retrieved 30 November 2020.
This article incorporates public domain material from "Entrez Gene: CYP11B1 cytochrome P450, family 11, subfamily B, polypeptide 1". Reference Sequence collection. National Center for Biotechnology Information. Retrieved 30 November 2020. This gene encodes a member of the cytochrome P450 superfamily of enzymes. The cytochrome P450 proteins are monooxygenases which catalyze many reactions involved in drug metabolism and synthesis of cholesterol, steroids and other lipids. This protein localizes to the mitochondrial inner membrane and is involved in the conversion of progesterone to cortisol in the adrenal cortex. Mutations in this gene cause congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 11-beta-hydroxylase deficiency. Transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been noted for this gene.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain. - ^ Zöllner A, Kagawa N, Waterman MR, Nonaka Y, Takio K, Shiro Y, et al. (February 2008). "Purification and functional characterization of human 11beta hydroxylase expressed in Escherichia coli". The FEBS Journal. 275 (4): 799–810. doi:10.1111/j.1742-4658.2008.06253.x. PMID 18215163. S2CID 45997341.
- ^ Dörr HG, Kuhnle U, Holthausen H, Bidlingmaier F, Knorr D (November 1984). "Etomidate: a selective adrenocortical 11 beta-hydroxylase inhibitor". Klinische Wochenschrift. 62 (21): 1011–3. doi:10.1007/bf01711722. PMID 6096625. S2CID 20077711.
- ^ Lake CL (7 December 2004). Pediatric Cardiac Anesthesia. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 68. ISBN 978-0-7817-5175-9. Retrieved 30 April 2012.
- ^ White PC, Curnow KM, Pascoe L (August 1994). "Disorders of steroid 11 beta-hydroxylase isozymes". Endocrine Reviews. 15 (4): 421–38. doi:10.1210/edrv-15-4-421. PMID 7988480.
- ^ White PC, Curnow KM, Pascoe L (1993). "Steroid 11β-Hydroxylase Isozymes (CYP11B1 and CYP11B2)". Cytochrome P450. Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology. Vol. 105. Springer. pp. 641–650. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-77763-9_41. ISBN 978-3-642-77765-3. S2CID 81304246.
- ^ a b c d Gupta V (October 2011). "Mineralocorticoid hypertension". Indian Journal of Endocrinology and Metabolism. 15 Suppl 4 (8): S298–312. doi:10.4103/2230-8210.86972. PMC 3230101. PMID 22145132.
- ^ a b c d e Strushkevich N, Gilep AA, Shen L, Arrowsmith CH, Edwards AM, Usanov SA, Park HW (February 2013). "Structural insights into aldosterone synthase substrate specificity and targeted inhibition". Molecular Endocrinology. 27 (2): 315–24. doi:10.1210/me.2012-1287. PMC 5417327. PMID 23322723.
- ^ a b c d e van Rooyen D, Gent R, Barnard L, Swart AC (April 2018). "The in vitro metabolism of 11β-hydroxyprogesterone and 11-ketoprogesterone to 11-ketodihydrotestosterone in the backdoor pathway". The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. 178: 203–212. doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2017.12.014. PMID 29277707. S2CID 3700135.
- ^ Mello, Penachioni, Amaral, Castro (October 2004). "11beta-hydroxylase deficiency". Arquivos Brasileiros de Endocrinologia e Metabologia (in Portuguese). 48 (5): 713–23. doi:10.1590/s0004-27302004000500018. PMID 15761543.
- ^ Bulsari K, Falhammar H (January 2017). "Clinical perspectives in congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 11β-hydroxylase deficiency". Endocrine. 55 (1): 19–36. doi:10.1007/s12020-016-1189-x. PMID 27928728. S2CID 11153844.
- ^ a b c Turcu AF, Rege J, Chomic R, Liu J, Nishimoto HK, Else T, et al. (June 2015). "Profiles of 21-Carbon Steroids in 21-hydroxylase Deficiency". The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism. 100 (6): 2283–90. doi:10.1210/jc.2015-1023. PMC 4454804. PMID 25850025.
- ^ Masiutin MM, Yadav MK (3 April 2023). "Alternative androgen pathways" (PDF). WikiJournal of Medicine. 10: 29. doi:10.15347/WJM/2023.003. S2CID 257943362.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is available under the CC BY 4.0 license.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is available under the CC BY 4.0 license. - ^ Bloem LM, Storbeck KH, Schloms L, Swart AC (October 2013). "11β-hydroxyandrostenedione returns to the steroid arena: biosynthesis, metabolism and function". Molecules. 18 (11). MDPI AG: 13228–44. doi:10.3390/molecules181113228. PMC 6270415. PMID 24165582.
- ^ Storbeck KH, Mostaghel EA (2019). "Canonical and Noncanonical Androgen Metabolism and Activity". Prostate Cancer. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology. Vol. 1210. Springer. pp. 239–277. doi:10.1007/978-3-030-32656-2_11. ISBN 978-3-030-32655-5. PMID 31900912. S2CID 209748543.
CYP11B1 and 2 have also been shown to 11β-hydroxylate T, yielding 11β-hydroxytestosterone (11OHT), though the levels produced by the adrenal are low due to the limited availability of adrenal derived T
- ^ Stárka L, Dušková M, Vítků J (September 2020). "11-Keto-testosterone and other androgens of adrenal origin". Physiological Research. 69 (Suppl 2): S187–S192. doi:10.33549/physiolres.934516. PMC 8603739. PMID 33094617.
- ^ a b Freel EM, Shakerdi LA, Friel EC, Wallace AM, Davies E, Fraser R, Connell JM (September 2004). "Studies on the origin of circulating 18-hydroxycortisol and 18-oxocortisol in normal human subjects". The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism. 89 (9): 4628–33. doi:10.1210/jc.2004-0379. PMC 1283128. PMID 15356073.
- ^ Nicod J, Dick B, Frey FJ, Ferrari P (February 2004). "Mutation analysis of CYP11B1 and CYP11B2 in patients with increased 18-hydroxycortisol production". Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology. 214 (1–2): 167–74. doi:10.1016/j.mce.2003.10.056. PMID 15062555. S2CID 617448.
- ^ Lenders JW, Williams TA, Reincke M, Gomez-Sanchez CE (January 2018). "DIAGNOSIS OF ENDOCRINE DISEASE: 18-Oxocortisol and 18-hydroxycortisol: is there clinical utility of these steroids?". European Journal of Endocrinology. 178 (1): R1–R9. doi:10.1530/EJE-17-0563. PMC 5705277. PMID 28904009.
- ^ Hanukoglu I, Privalle CT, Jefcoate CR (May 1981). "Mechanisms of ionic activation of adrenal mitochondrial cytochromes P-450scc and P-45011 beta" (PDF). J. Biol. Chem. 256 (9): 4329–35. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(19)69437-8. PMID 6783659. Archived (PDF) from the original on 16 September 2012. Retrieved 21 July 2012.
- ^ Rapoport R, Sklan D, Hanukoglu I (March 1995). "Electron leakage from the adrenal cortex mitochondrial P450scc and P450c11 systems: NADPH and steroid dependence". Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 317 (2): 412–6. doi:10.1006/abbi.1995.1182. PMID 7893157. Archived from the original on 20 May 2020. Retrieved 26 June 2019.
- ^ Hanukoglu I, Feuchtwanger R, Hanukoglu A (November 1990). "Mechanism of corticotropin and cAMP induction of mitochondrial cytochrome P450 system enzymes in adrenal cortex cells" (PDF). J. Biol. Chem. 265 (33): 20602–8. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(17)30545-8. PMID 2173715. Archived (PDF) from the original on 16 September 2012. Retrieved 21 July 2012.
- ^ Miller WL (2019). "Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia: Time to Replace 17OHP with 21-Deoxycortisol". Hormone Research in Paediatrics. 91 (6): 416–420. doi:10.1159/000501396. PMID 31450227. S2CID 201733086.
- ^ Greaves RF, Kumar M, Mawad N, Francescon A, Le C, O'Connell M, Chi J, Pitt J (October 2023). "Best Practice for Identification of Classical 21-Hydroxylase Deficiency Should Include 21 Deoxycortisol Analysis with Appropriate Isomeric Steroid Separation". Int J Neonatal Screen. 9 (4): 58. doi:10.3390/ijns9040058. PMC 10594498. PMID 37873849.
Further reading
- Helmberg A (August 1993). "Twin genes and endocrine disease: CYP21 and CYP11B genes". Acta Endocrinol. 129 (2): 97–108. doi:10.1530/acta.0.1290097. PMID 8372604.
- Stowasser M, Gunasekera TG, Gordon RD (December 2001). "Familial varieties of primary aldosteronism". Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 28 (12): 1087–90. doi:10.1046/j.1440-1681.2001.03574.x. PMID 11903322. S2CID 23091842.
- Helmberg A, Ausserer B, Kofler R (November 1992). "Frame shift by insertion of 2 basepairs in codon 394 of CYP11B1 causes congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to steroid 11 beta-hydroxylase deficiency". J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 75 (5): 1278–81. doi:10.1210/jcem.75.5.1430088. PMID 1430088.
- Pascoe L, Curnow KM, Slutsker L, Connell JM, Speiser PW, New MI, White PC (September 1992). "Glucocorticoid-suppressible hyperaldosteronism results from hybrid genes created by unequal crossovers between CYP11B1 and CYP11B2". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 89 (17): 8327–31. Bibcode:1992PNAS...89.8327P. doi:10.1073/pnas.89.17.8327. PMC 49911. PMID 1518866.
- Kawamoto T, Mitsuuchi Y, Toda K, Yokoyama Y, Miyahara K, Miura S, Ohnishi T, Ichikawa Y, Nakao K, Imura H (February 1992). "Role of steroid 11 beta-hydroxylase and steroid 18-hydroxylase in the biosynthesis of glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids in humans". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 89 (4): 1458–62. Bibcode:1992PNAS...89.1458K. doi:10.1073/pnas.89.4.1458. PMC 48470. PMID 1741400.
- White PC, Dupont J, New MI, Leiberman E, Hochberg Z, Rösler A (May 1991). "A mutation in CYP11B1 (Arg-448----His) associated with steroid 11 beta-hydroxylase deficiency in Jews of Moroccan origin". J. Clin. Invest. 87 (5): 1664–7. doi:10.1172/JCI115182. PMC 295260. PMID 2022736.
- Kawamoto T, Mitsuuchi Y, Toda K, Miyahara K, Yokoyama Y, Nakao K, Hosoda K, Yamamoto Y, Imura H, Shizuta Y (September 1990). "Cloning of cDNA and genomic DNA for human cytochrome P-45011 beta". FEBS Lett. 269 (2): 345–9. doi:10.1016/0014-5793(90)81190-Y. PMID 2401360. S2CID 35151332.
- Mornet E, Dupont J, Vitek A, White PC (December 1989). "Characterization of two genes encoding human steroid 11 beta-hydroxylase (P-450(11) beta)". J. Biol. Chem. 264 (35): 20961–7. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(19)30030-4. PMID 2592361.
- Chua SC, Szabo P, Vitek A, Grzeschik KH, John M, White PC (October 1987). "Cloning of cDNA encoding steroid 11 beta-hydroxylase (P450c11)". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 84 (20): 7193–7. Bibcode:1987PNAS...84.7193C. doi:10.1073/pnas.84.20.7193. PMC 299256. PMID 3499608.
- Naiki Y, Kawamoto T, Mitsuuchi Y, Miyahara K, Toda K, Orii T, Imura H, Shizuta Y (December 1993). "A nonsense mutation (TGG [Trp116]-->TAG [Stop]) in CYP11B1 causes steroid 11 beta-hydroxylase deficiency". J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 77 (6): 1677–82. doi:10.1210/jcem.77.6.7903314. PMID 7903314.
- Joehrer K, Geley S, Strasser-Wozak EM, Azziz R, Wollmann HA, Schmitt K, Kofler R, White PC (October 1997). "CYP11B1 mutations causing non-classic adrenal hyperplasia due to 11 beta-hydroxylase deficiency". Hum. Mol. Genet. 6 (11): 1829–34. doi:10.1093/hmg/6.11.1829. PMID 9302260.
- Cargill M, Altshuler D, Ireland J, Sklar P, Ardlie K, Patil N, Shaw N, Lane CR, Lim EP, Kalyanaraman N, Nemesh J, Ziaugra L, Friedland L, Rolfe A, Warrington J, Lipshutz R, Daley GQ, Lander ES (July 1999). "Characterization of single-nucleotide polymorphisms in coding regions of human genes". Nat. Genet. 22 (3): 231–8. doi:10.1038/10290. PMID 10391209. S2CID 195213008.
- Halushka MK, Fan JB, Bentley K, Hsie L, Shen N, Weder A, Cooper R, Lipshutz R, Chakravarti A (July 1999). "Patterns of single-nucleotide polymorphisms in candidate genes for blood-pressure homeostasis". Nat. Genet. 22 (3): 239–47. doi:10.1038/10297. PMID 10391210. S2CID 4636523.
- Cao PR, Bernhardt R (June 1999). "Interaction of CYP11B1 (cytochrome P-45011 beta) with CYP11A1 (cytochrome P-450scc) in COS-1 cells". Eur. J. Biochem. 262 (3): 720–6. doi:10.1046/j.1432-1327.1999.00414.x. PMID 10411633.
- Loidi L, Quinteiro C, Barros F, Domínguez F, Barreiro J, Pombo M (December 1999). "The C494F variant in the CYP11B1 gene is a sequence polymorphism in the Spanish population". J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 84 (12): 4749. doi:10.1210/jcem.84.12.6272-6. PMID 10599751.
- Chabre O, Portrat-Doyen S, Chaffanjon P, Vivier J, Liakos P, Labat-Moleur F, Chambaz E, Morel Y, Defaye G (November 2000). "Bilateral laparoscopic adrenalectomy for congenital adrenal hyperplasia with severe hypertension, resulting from two novel mutations in splice donor sites of CYP11B1". J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 85 (11): 4060–8. doi:10.1210/jcem.85.11.6897. PMID 11095433.
- Fisher A, Friel EC, Bernhardt R, Gomez-Sanchez C, Connell JM, Fraser R, Davies E (September 2001). "Effects of 18-hydroxylated steroids on corticosteroid production by human aldosterone synthase and 11beta-hydroxylase". J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 86 (9): 4326–9. doi:10.1210/jcem.86.9.7797. PMID 11549669.
- Hampf M, Dao NT, Hoan NT, Bernhardt R (September 2001). "Unequal crossing-over between aldosterone synthase and 11beta-hydroxylase genes causes congenital adrenal hyperplasia". J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 86 (9): 4445–52. doi:10.1210/jcem.86.9.7820. PMID 11549691.
External links
- Steroid+11-beta-hydroxylase at the U.S. National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- v
- t
- e