| ZBTB7A |
|---|
 |
| Available structures |
|---|
| PDB | Ortholog search: PDBe RCSB |
|---|
| List of PDB id codes |
|---|
2IF5, 2NN2 |
|
|
| Identifiers |
|---|
| Aliases | ZBTB7A, FBI-1, FBI1, LRF, ZBTB7, ZNF857A, pokemon, TIP21, zinc finger and BTB domain containing 7A, MNDLFH |
|---|
| External IDs | OMIM: 605878; MGI: 1335091; HomoloGene: 7820; GeneCards: ZBTB7A; OMA:ZBTB7A - orthologs |
|---|
| Gene location (Human) |
|---|
 | | Chr. | Chromosome 19 (human)[1] |
|---|
| | Band | 19p13.3 | Start | 4,043,303 bp[1] |
|---|
| End | 4,066,899 bp[1] |
|---|
|
| Gene location (Mouse) |
|---|
 | | Chr. | Chromosome 10 (mouse)[2] |
|---|
| | Band | 10|10 C1 | Start | 80,971,054 bp[2] |
|---|
| End | 80,988,829 bp[2] |
|---|
|
| RNA expression pattern |
|---|
| Bgee | | Human | Mouse (ortholog) |
|---|
| Top expressed in | - nipple
- internal globus pallidus
- middle temporal gyrus
- pylorus
- cerebellar vermis
- Brodmann area 23
- cardia
- vulva
- superior surface of tongue
- ventral tegmental area
|
| | Top expressed in | - ascending aorta
- aortic valve
- inner renal medulla
- superior frontal gyrus
- glomerulus
- lip
- granulocyte
- right kidney
- esophagus
- cerebellar cortex
|
| | More reference expression data |
|
|---|
| BioGPS | 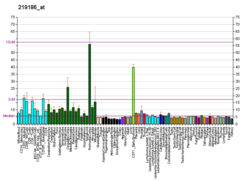

 | | More reference expression data |
|
|---|
|
| Gene ontology |
|---|
| Molecular function | - RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding
- DNA binding
- DNA-binding transcription repressor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific
- protein binding
- histone acetyltransferase binding
- metal ion binding
- nucleic acid binding
- DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific
- transcription corepressor binding
- DNA-binding transcription factor activity
- transcription corepressor activity
- sequence-specific DNA binding
- SMAD binding
- androgen receptor binding
| | Cellular component | - nucleus
- cytoplasm
- NuRD complex
- site of double-strand break
- DNA-dependent protein kinase complex
| | Biological process | - multicellular organism development
- cell differentiation
- negative regulation of transcription, DNA-templated
- regulation of transcription, DNA-templated
- negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II
- transcription, DNA-templated
- regulation of alternative mRNA splicing, via spliceosome
- regulation of glycolytic process
- chromatin organization
- chromatin remodeling
- cellular response to DNA damage stimulus
- B cell differentiation
- negative regulation of transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway
- protein localization to nucleus
- regulation of apoptotic process
- erythrocyte maturation
- fat cell differentiation
- negative regulation of Notch signaling pathway
- regulation of DNA-binding transcription factor activity
- positive regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity
- negative regulation of androgen receptor signaling pathway
- double-strand break repair via classical nonhomologous end joining
- regulation of transcription regulatory region DNA binding
| | Sources:Amigo / QuickGO |
|
| Orthologs |
|---|
| Species | Human | Mouse |
|---|
| Entrez | | |
|---|
| Ensembl | | |
|---|
| UniProt | | |
|---|
| RefSeq (mRNA) | |
|---|
NM_015898
NM_001317990
NM_020224 |
| |
|---|
| RefSeq (protein) | | NP_034861
NP_001391790
NP_001391791
NP_001391792
NP_001391793
|
|---|
NP_001391794
NP_001391795
NP_001391796 |
|
|---|
| Location (UCSC) | Chr 19: 4.04 – 4.07 Mb | Chr 10: 80.97 – 80.99 Mb |
|---|
| PubMed search | [3] | [4] |
|---|
|
| Wikidata |
| View/Edit Human | View/Edit Mouse |
|

 2if5: Structure of the POZ domain of human LRF, a master regulator of oncogenesis
2if5: Structure of the POZ domain of human LRF, a master regulator of oncogenesis 2nn2: Crystal structure of the BTB domain from the LRF/ZBTB7 transcriptional regulator
2nn2: Crystal structure of the BTB domain from the LRF/ZBTB7 transcriptional regulator